During the Inflammatory Response Histamine May Be Released by
Subsequently one may also ask is histamine released during inflammation. Challenges with an eosinophilic influx tended to be associated with higher concentrations of histamine than neutrophilic influxes.
The Inflammatory Response Youtube
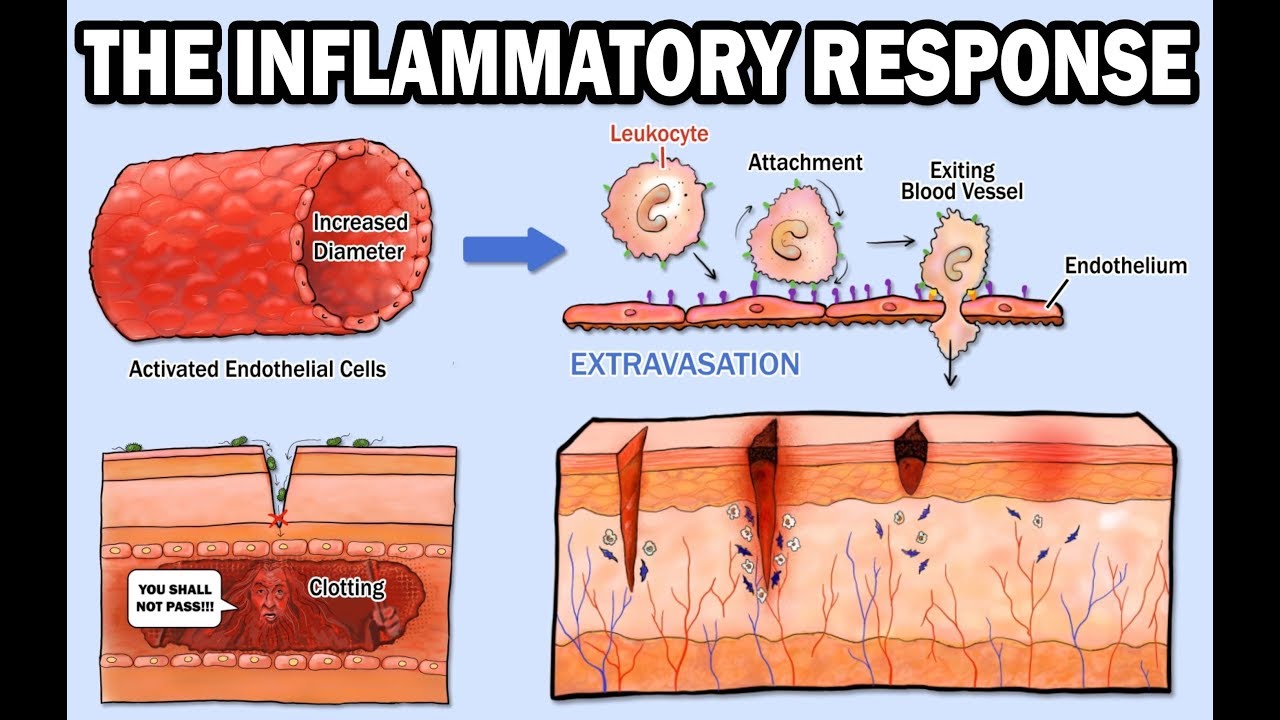
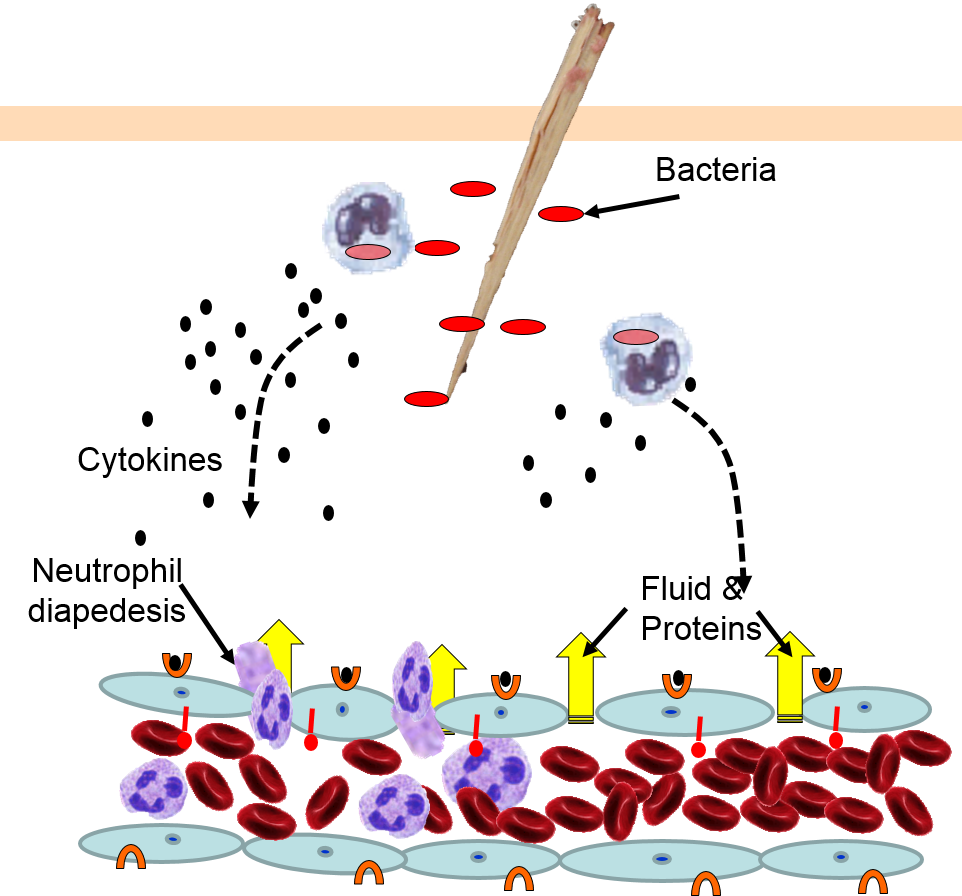
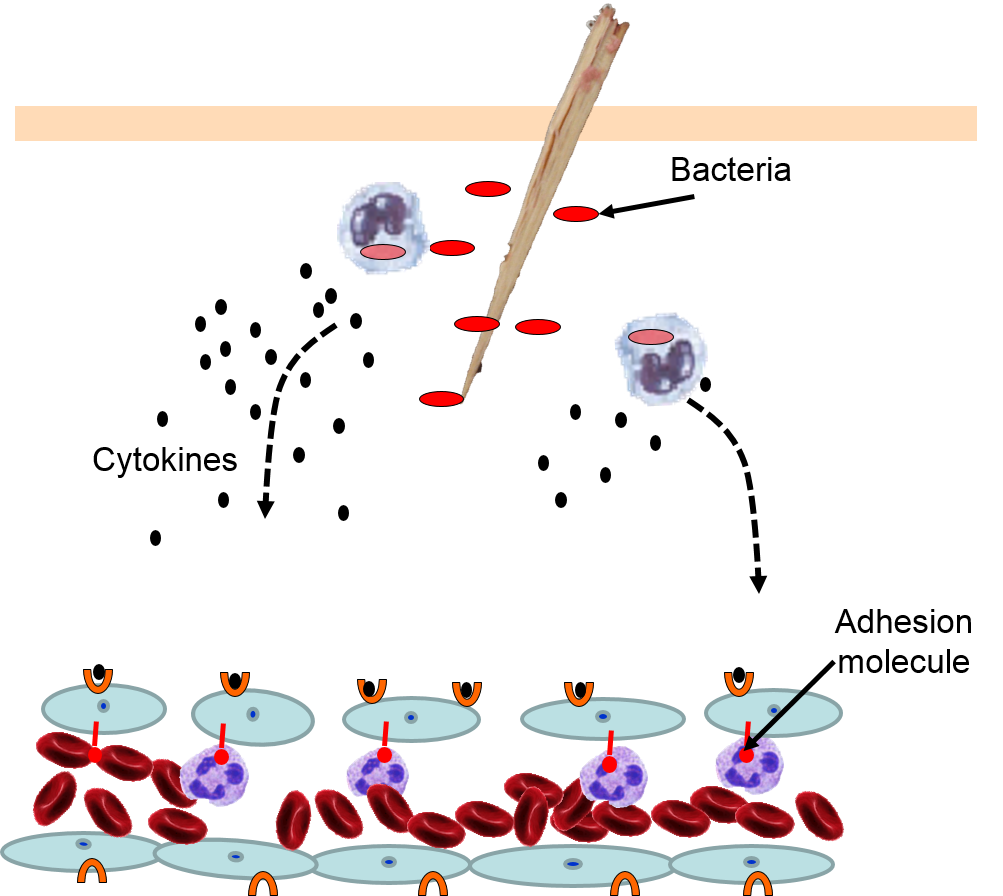
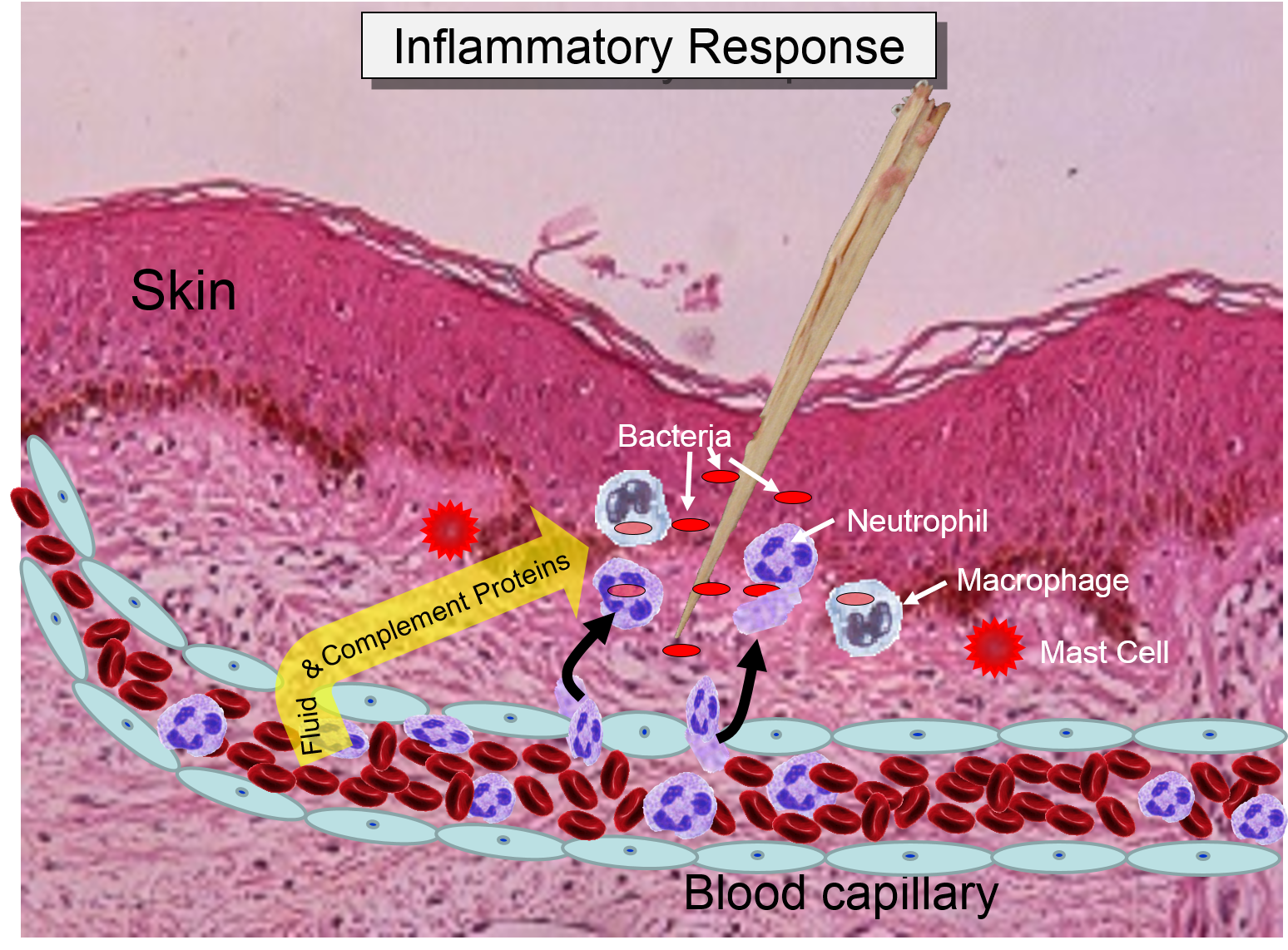
During the inflammatory response histamine is released by damaged cells which attracts phagocytes to the region.

. Those fish can build up high levels. Histamine is released by mast cells as an immune response and is later degraded primarily by two enzymes. Other mediators act as regulatory components to establish homeostasis after injury or prevent the inflammatory process.
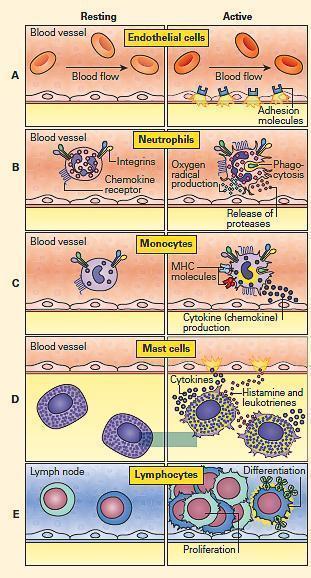
Activated mast cell release a variety of inflammatory mediators including cytokines chemokines histamine proteases prostaglandins leukotrienes and serglycin proteoglycans. This increases blood flow to affected areas to flood them with immune cells. Some people may be sensitive to that.
This helps isolate the foreign substance. The exact role s of histamine in the exercise response is largely unknown and understudied. However it is unknown what it is specifically about exercise that causes the release of histamine.
These chemicals cause blood vessels to leak fluid into the tissues causing swelling. Superantigens are bacterial or viral proteins that can cause an excessive activation of T cells from the specific adaptive immune defense as well as an excessive release of cytokines that overstimulates the inflammatory response. Similar to the immediate skin response the early allergic response in the nose demonstrated a cell influx with release of histamine.
Histamine is a vasoactive amine that plays an important role in the early acute inflammatory response. Diamine oxidase DAO coded by AOC1 genes and histamine-N-methyltransferase HNMT. Histamine is commonly associated with immune responses typically involved in allergic reactions.
Inflammation a blanket term describing an immune response triggers the release of histamine in the body. The damaged cells release chemicals including histamine bradykinin and prostaglandins. This release is not dependent on myeloperoxidase but on other oxidative metabolites since myeloperoxidase-deficient neutrophils also induce histamine release.
The inflammatory response inflammation occurs when tissues are injured by bacteria trauma toxins heat or any other cause. Reduction of IgE overproduction may lower the likelihood of allergens finding sufficient free IgE to trigger a mast-cell-release of histamine. Heparin plays a key role in allergic and inflammatory reactions driven by mast cells scientists show.
Multiple groups have demonstrated that platelets impact inflammatory processes from atherosclerosis to infection. Histamines function in physiological contexts outside of exercise such as its role in the. A significant inverse relationship exists between ascorbate and histamine in the ACS versus C groups P 001 and the SCAD versus C groups P 001.
These data reveal that release of histamine and activation of H 1 and H 2 receptors during recovery from exercise appears to upregulate pathways related to inflammation endothelial and vascular function metabolism and cell maintenance. Sites of histamine release Much of the histamine in the body is produced by the granules in mast cells and basophils as part of a local immune response to the presence of invading bodies. Nasal cellular inflammation therefore can occur within minutes of allergen exposure.
The inflammatory response to bacterial superantigens is one scenario in which a life-threatening fever may develop. In the gastrointestinal tract histamine is present in relatively high concentrations especially during inflammatory reactions. Histamine is stored in the.
This biogenic amine acts on a variety of cell types including smooth muscle cells neurons endocrine and exocrine cells blood cells and cells of the immune system 6. Which leukocytes release histamine during the inflammatory response quizlet. This attraction by a chemical is called ___.
While these effects help the body fight infections both long-term and acute inflammation is increasingly linked to depression. Basophils contain histamine which promotes vasodilation and enhances migration of leukocytes to inflammatory sites. It can be released in multiple tissues including skeletal muscle during exercise.
Histamine and isoprostane levels increase in SCAD and ACS patients. Histamine initiates abnormal immune response leading to cytokine storm and multi-organs failure. These experiments show that mast cells exposed to immune complexes and activated neutrophils or eosinophils may augment the inflammatory response.
The inflammatory response In response to injury and infection specialised immune cells called mast cells release histamine. Histamine a biogenic amine commonly associated with the immune and inflammatory response is produced and released within skeletal muscle during exercise. Inflammatory mediators including cytokines histamine bradykinin prostaglandins and leukotrienes impact the immune system usually as proinflammatory factors.
Mast cell activation and lipid oxidation generated during atherosclerosis manifest this inflammatory response. These transcriptome-level changes suggest that there is indeed cross-talk between histaminergic and inflammatory signaling and also. Histamine is a main mediator that is being released by immune system and other cells as a result of virus invasions or activation.
It can influence numerous functions of the cells involved in the re. Histamine is not only the major mediator of the acute inflammatory and immediate hypersensitivity responses but has also been demonstrated to affect chronic inflammation and regulate several essential events in the immune response. Chemical mediators of inflammation Stored in granules of circulating basophils and mast cells histamine is.
Histamine also modulates the inflammatory response by acting on other cellular populations in human lung macrophages binding of histamine to H1R induces production of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 and β-glucuronidase 37 38 a marker of exocytosis and the release of lysosomal enzymes is associated with epithelial damage and rupture of the. Histamine causes blood vessels to widen vasodilation. To date a total of three histamine receptors H 1 H 2 and H 3 have been discovered in human gut1415.
The study sheds some new light on the biological function of heparin. What cell releases histamine promotes inflammation. Histamine poisoning can happen if you eat fish that werent kept at safe temperatures and spoiled before you got them.

Histamine In The Immune Regulation Of Allergic Inflammation Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Scheme Showing The Synergistic Activation Of Inflammatory Response In Download Scientific Diagram

Basophil An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Regulation Of The Immune Response And Inflammation By Histamine And Histamine Receptors Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Histamine An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Inflammatory Response Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

Biology Animal Structure And Function The Immune System Innate Immune Response Viva Open

Histamine Description Facts Britannica

Inflammation And Fever Microbiology Health And Disease

21 2 Barrier Defenses And The Innate Immune Response Anatomy Physiology




Comments
Post a Comment